Introduction to Goal 4 - Quality Education
Use this guide to introduce Global Goal 4, Quality Education to your students.

What is Global Goal 4?
Sustainable Development Goal 4: Quality Education is one of the 17 Sustainable Development Goals established by the United Nations in 2015. You can find out more about the Goals in our introductory guide.
Sustainable Development Goal 4 (SDG 4) is the education goal. It aims to ensure inclusive and equitable access to education and promote lifelong learning opportunities for all. Education helps us achieve many other goals. It can be a pathway to growth, a boost to public health and a stepping stone towards peace.
Активности
Below are some ideas to help bring Goal 4 to life for your students. They work as stand-alone activities or in sequence.
Activity 1: Exploring equal access to Quality Education
In this activity, students will be introduced to the concept of equality in terms of access to education.
Length - 15 min
Show your students this video discussing education.
Reflect on the video
Reflect on the video
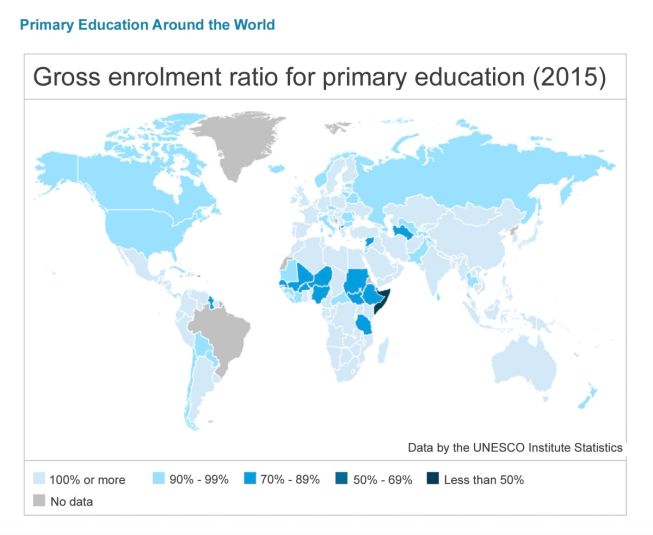
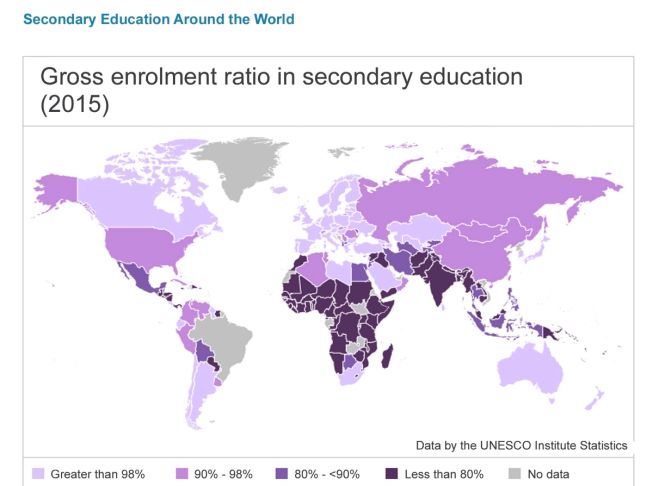
Investigate education equality through data
Investigate education equality through data
Discussion around maps
Discussion around maps

Activity 2: Be a fact-ivist - Dive into data
In this activity students will dive into data on education and create an infographic poster.
Length - 30 min
Investigate data facts
Investigate data facts
Infographic poster creation
Infographic poster creation

Activity 3: Exploring what helps and hinders learning
In this activity students will think about the different ways that children learn and what that means in terms of delivering a quality education for all children.
Length 45 min
Увод
Увод
Exploring how we learn
Exploring how we learn
Exploring our barriers to learning
Exploring our barriers to learning


The activities are created by World's Largest Lesson